Requête spatiale
Dans les options de carte, vous pouvez configurer les recherches d’adresses basées sur des services web externes (nominatim, google, IGN France). Lire Options de la carte — Les options générales de la carte. De plus, vous pouvez ajouter des moyens de recherche spatiale à Lizmap. Cela signifie que vous autoriserez les utilisateurs à effectuer des recherches avec des données spatiales, telles que les pays, les points d’intérêts, etc. Vous avez 2 manières pour ajouter des moyens de recherche dans Lizmap :
Vous pouvez créer une table ou une vue
lizmap_searchdans votre base de données PostgreSQL pour stocker les données de recherche de tous vos projets Lizmap.
Recherche PostgreSQL
Lorsque vous avez de nombreux projets et données, la meilleure solution pour fournir des capacités de recherche est de mettre en place une relation dédiée (table ou vue) dans votre base de données. Il est possible d’utiliser une base de données PostgreSQL pour stocker les données de recherche.
Pré-requis
Une base de données PostgreSQL, accessible depuis Lizmap Web Client.
PostgreSQL avec les extensions activées :
unaccentetpg_trgm(pour des requêtes LIKE efficaces)Une fonction personnalisée
f_unaccentqui peut être utilisée dans un index. Voir cette réponse Stack Overflow pour l’explication.
-- Add the extension pg_trgm
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pg_trgm;
-- Add the extension unaccent, available with PostgreSQL contrib tools.
-- This is needed to provide searches which are not sensitive to accentuated characters.
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS unaccent;
-- Add the f_unaccent function to be used in the index
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.f_unaccent(text)
RETURNS text AS
$func$
SELECT public.unaccent('public.unaccent', $1) -- schema-qualify function and dictionary
$func$ LANGUAGE sql IMMUTABLE;
Note
Nous avons choisi d’utiliser l’extension pg_trgm et sa fonction habituelle f_unaccent plutôt que l’outil de PostgreSQL de recherche plein texte (FTS), pour garder l’outil aussi simple que possible et éviter de devoir créer des vecteurs FTS pour votre recherche de données.
Lizmap Cloud
Astuce
Si l’instance est hébergée sur Lizmap Cloud  , lisez la documentation concernant une étape sur lizmap_search.
, lisez la documentation concernant une étape sur lizmap_search.
Créer la table de recherche Lizmap ou la vue
L’administrateur de la base de données doit créer une table, vue ou vue matérialisée nommée « lizmap_search ». Cette relation doit être accessible dans le search_path (vous pouvez la mettre dans le schéma public, ou configurer la variable search_path pour la base de données ou l’utilisateur qui se connecte à la base de données).
La relation lizmap_search doit contenir les colonnes suivantes :
« item_layer » (texte). Nom de la couche. Par exemple, « Pays »
item_label(texte). Étiquette pour afficher les résultats, c’est-à-dire les données parmi lesquelles effectuer la recherche. Ex : « France » ou « John Doe - Australie ». Vous pouvez le construire à partir d’une concaténation des valeurs de plusieurs champs.item_project(texte). Liste de projets Lizmap séparés par des virgules. Lorsqu’elle est définie, la recherche ne sera effectuée que pour les projets Lizmap spécifiés. La valeur peut êtreNULLsi vous ne voulez pas filtrer par projet.item_filter(texte). Nom d’utilisateur ou nom de groupe. Lorsqu’il est donné, les résultats seront filtrés en fonction du login de l’utilisateur authentifié et des groupes. Par exemple, “admins”. La valeur peut êtreNULLsi vous ne voulez pas filtrer par utilisateur.geom(géométrie). Nous conseillons de stocker toutes les géométries avec le même SRID.
Voici un exemple de code SQL que vous pouvez utiliser, pour ajouter des données issues de deux tables spatiales différentes dans la recherche lizmap (ici en tant que vue matérialisée pour faciliter une maintenance ultérieure)
DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW IF EXISTS lizmap_search;
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW lizmap_search AS
SELECT
'Commune' AS item_layer, -- name of the layer presented to the user
concat(idu, ' - ', tex2) AS item_label, -- the search label is a concatenation between the 'Commune' code (idu) and its name (tex2)
NULL AS item_filter, -- the data will be searchable for every Lizmap user
NULL AS item_project, -- the data will be searchable for every Lizmap maps (published QGIS projects)
geom -- geometry of the 'Commune'. You could also use a simplified version, for example: ST_Envelope(geom) AS geom
FROM cadastre.geo_commune
UNION ALL -- combine the data between the 'Commune' (above) and the 'Parcelles' (below) tables
SELECT
'Parcelles' AS item_layer,
concat(code, ' - ', proprietaire) AS item_label,
'admins' AS item_filter, -- only users in the admins Lizmap group will be able to search among the 'Parcelles'
'cadastre,urban' AS item_project, -- the Parcelles will be available in search only for the cadastre.qgs and urban.qgs QGIS projects
geom
FROM cadastre.parcelle_info
;
Optimisation
Vous devriez utiliser une table, ou une vue matérialisée sur laquelle vous pouvez ajouter des index pour accélérer les requêtes de recherche.
Nous vous conseillons vivement d’ajouter un index trigramme sur le champ non accentué
item_label, pour accélérer la requête de recherche :
-- Create the index on the unaccentuated item_label column:
DROP INDEX IF EXISTS lizmap_search_idx;
CREATE INDEX lizmap_search_idx ON lizmap_search USING GIN (f_unaccent(item_label) gin_trgm_ops);
-- You can refresh the materialized view at any time (for example in a cron job) with:
REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW lizmap_search;
Avertissement
Actuellement, la recherche Lizmap PostgreSQL ne peut pas utiliser les géométries 3D, ou les géométries avec des valeurs Z ou M. Vous devez utiliser la fonction ST_Force2D(geom) pour convertir les géométries en géométries 2D.
Configurer l’accès
Une fois que cette table (ou vue ou vue matérialisée) est créée dans votre base de données, vous devez vérifier que Lizmap a un accès en lecture dessus.
Si votre instance de Lizmap utilise PostgreSQL pour stocker les utilisateurs, groupes et droits, un profil de connexion existe déjà pour votre base de données. Vous pouvez alors simplement ajouter la relation lizmap_search dans cette base de données (dans le schéma public).
Si ce n’est pas le cas, ou si vous avez besoin de placer les données de recherche dans une autre base de données (ou de vous connecter avec un autre utilisateur PostgreSQL), vous devez ajouter un nouveau profil de connexion à la base de données dans le fichier de configuration de Lizmap lizmap/var/config/profiles.ini.php. Le nouveau profil est une nouvelle section préfixée jdb, appelée jdb:search. Par exemple, ajoutez la section suivante (remplacez les variables DATABASE_ par les valeurs correctes) :
[jdb:search]
driver="pgsql"
database=DATABASE_NAME
host=DATABASE_HOST
user=DATABASE_USER
password=DATABASE_PASSWORD
; search_path=DATABASE_SCHEMA_WITH_LIZMAP_SEARCH,public
Vous n’avez pas besoin de configurer l’outil localiser par couche. Le lien avec Lizmap Web Client se fait automatiquement si vous pouvez exécuter la requête ci-dessous avec succès dans PgAdmin en utilisant les mêmes informations d’identification que l’application Lizmap. Vous ne devez pas spécifier le schéma où se trouve la table lizmap_search. Elle doit fonctionner sans spécifier le schéma.
SELECT * FROM lizmap_search LIMIT 1;
Vous pouvez maintenant utiliser la barre de recherche par défaut dans Lizmap qui se trouve dans le coin supérieur droit.
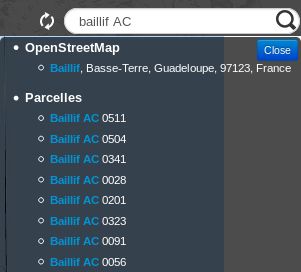
Debug côté client
Visitez une carte sur laquelle vous avez activé
lizmap_search.En appuyant sur F12 dans votre navigateur web, vous pouvez voir les requêtes HTTP effectuées dans l’onglet Network.
Effacer toutes les requêtes HTTP, ce n’est pas obligatoire, mais ce sera plus facile.
Lorsque vous appuyez sur Enter dans la boîte de recherche après avoir écrit du texte, une requête HTTP ciblant
index.php/lizmap/searchFts/get?doit être lancée.Cliquez avec le bouton droit de la souris pour l’ouvrir dans un nouvel onglet et modifiez la requête HTTP en ajoutant
&debug=trueà la fin.Vous pouvez voir la requête SQL générée dans votre .
En cas d’erreur, pensez à vérifier vos logs.
